Tips for Choosing an Excavator Demolition Attachment to Boost Productivity
With hundreds of sizes and styles of Demolition Attachments on the market — from small grapples to massive pulverizers — it's not as easy as picking one, attaching it to an excavator and expecting top production. Like a good beer, some tools just fit better at different times.
Knock out jobs faster by refining the demolition attachment selection process. Consider the application, the carrier, the return on investment and more to determine the perfect match.
Making the Perfect Match
First, consider the type of work the attachment will perform. From primary to secondary demolition and from rebar-enforced concrete to wood and brick, the application should be the first factor to guide an attachment choice.
When starting to demolish a structure, multi-quick processors, shears, crushers, pulverizers and demolition grapples tend to be the top picks for primary demolition. The choice between them depends on the type of material and how it needs to be broken up.
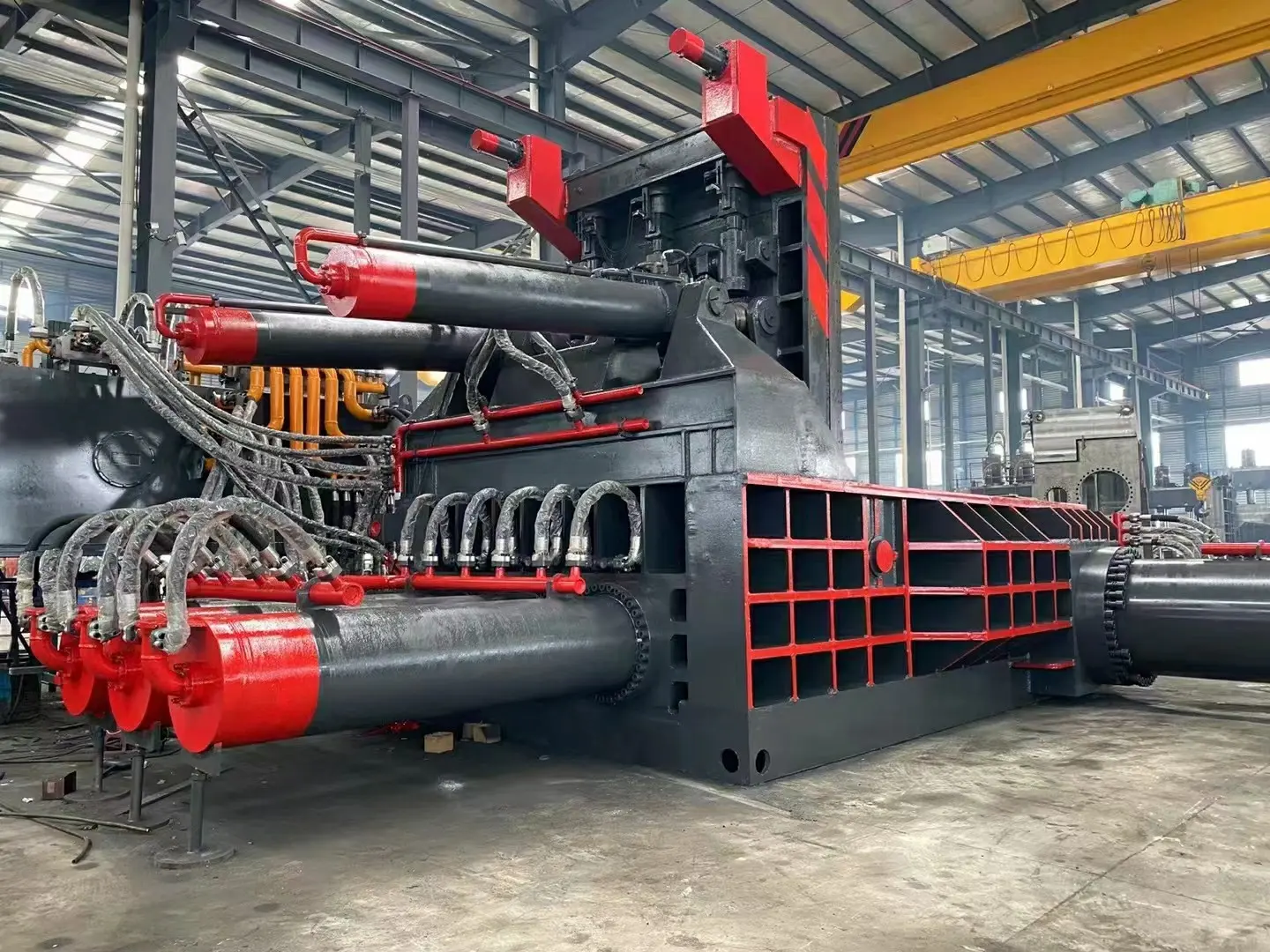
Crusher and pulverizer attachments, for example, tackle jobs best made up of mostly concrete. Choose a crusher — or "cracker" — if the structure is composed of concrete with little or no rebar and if it's necessary to break the concrete into chunks large enough for easy sorting and recycling. A pulverizer attachment better handles concrete that's heavily reinforced with rebar. Unlike the crusher attachment, the pulverizer will break the concrete into small pieces and cut through the embedded rebar, allowing the concrete to fall to the ground rather than hang onto the rebar.
Pulverizers can also break concrete into manageable sizes during secondary demolition. If the demolition involves both crushing concrete and cutting steel, contractors should consider combi-crushers that incorporate both cutting edges and teeth.
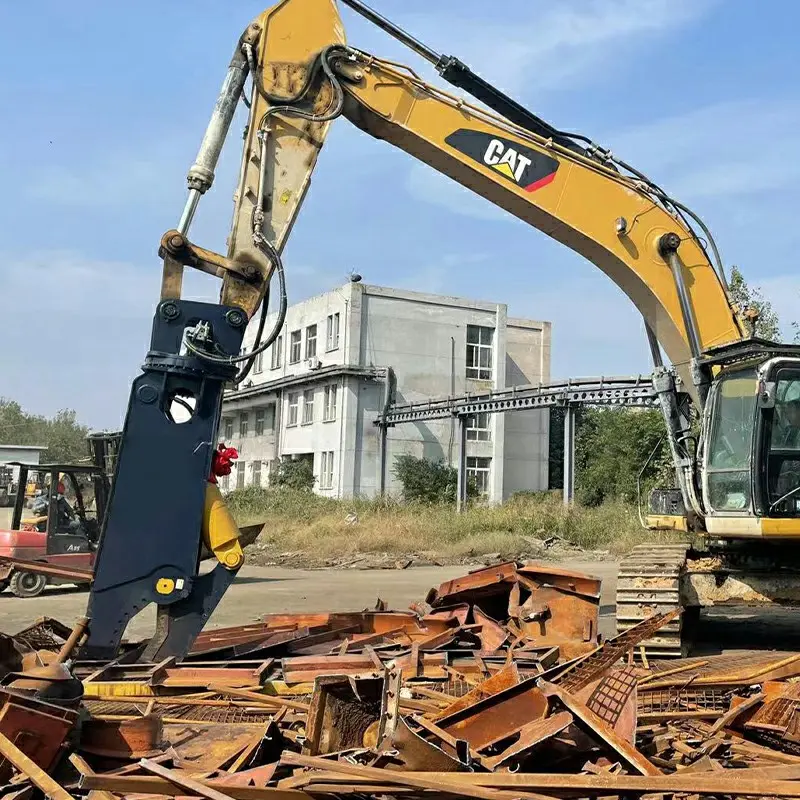
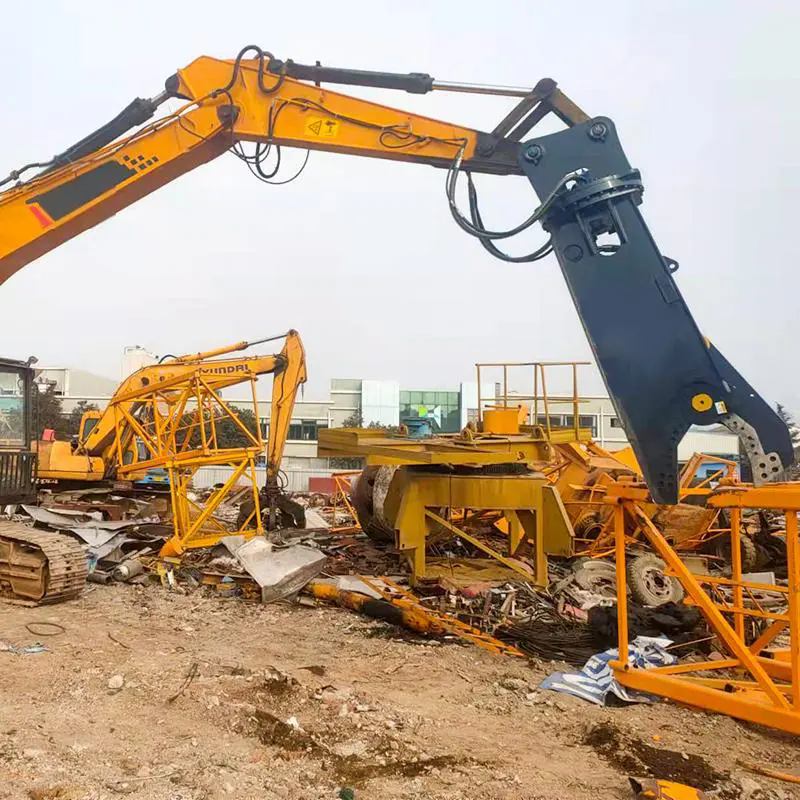
If concrete isn’t part of the demolition picture but steel is, a demolition processor with shear jaws or a mobile Shear Attachment will work best since they cut through steel better than a tool meant for multiple types of material.
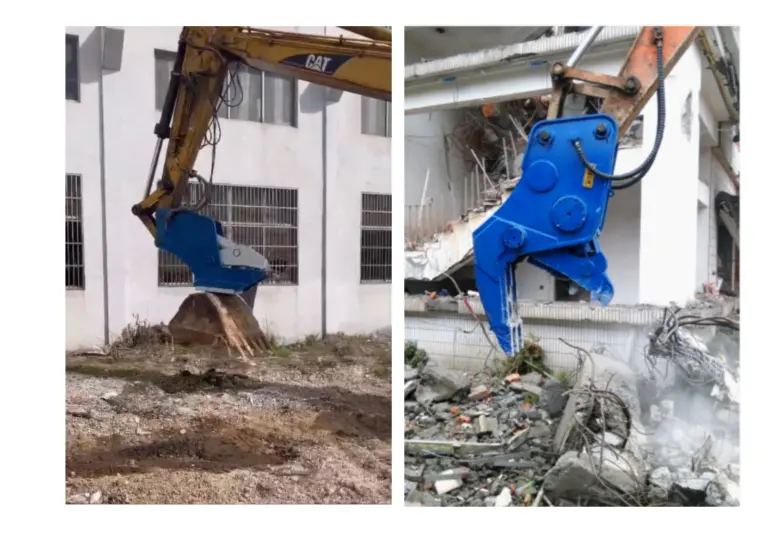
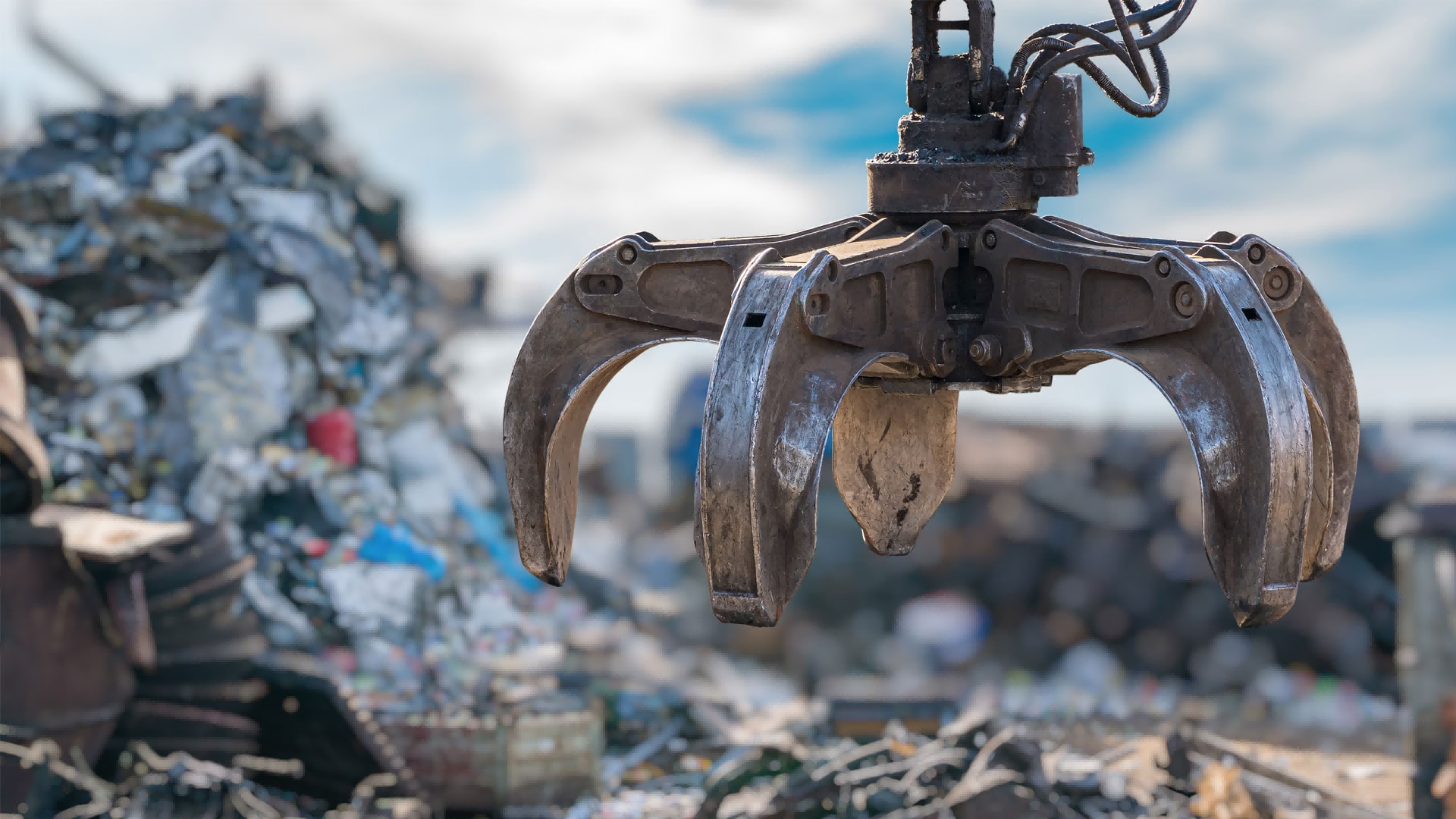
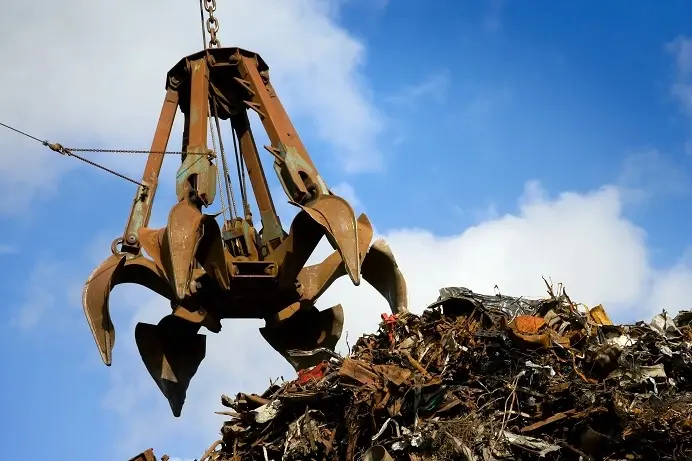
When working jobs with light materials — such as wood and brick, commonly found in residential demolition — use a demolition grapple. Besides breaking apart materials, rotating grapples work well for sorting during secondary demolition, and increase versatility and productivity by allowing a wide range of movement.
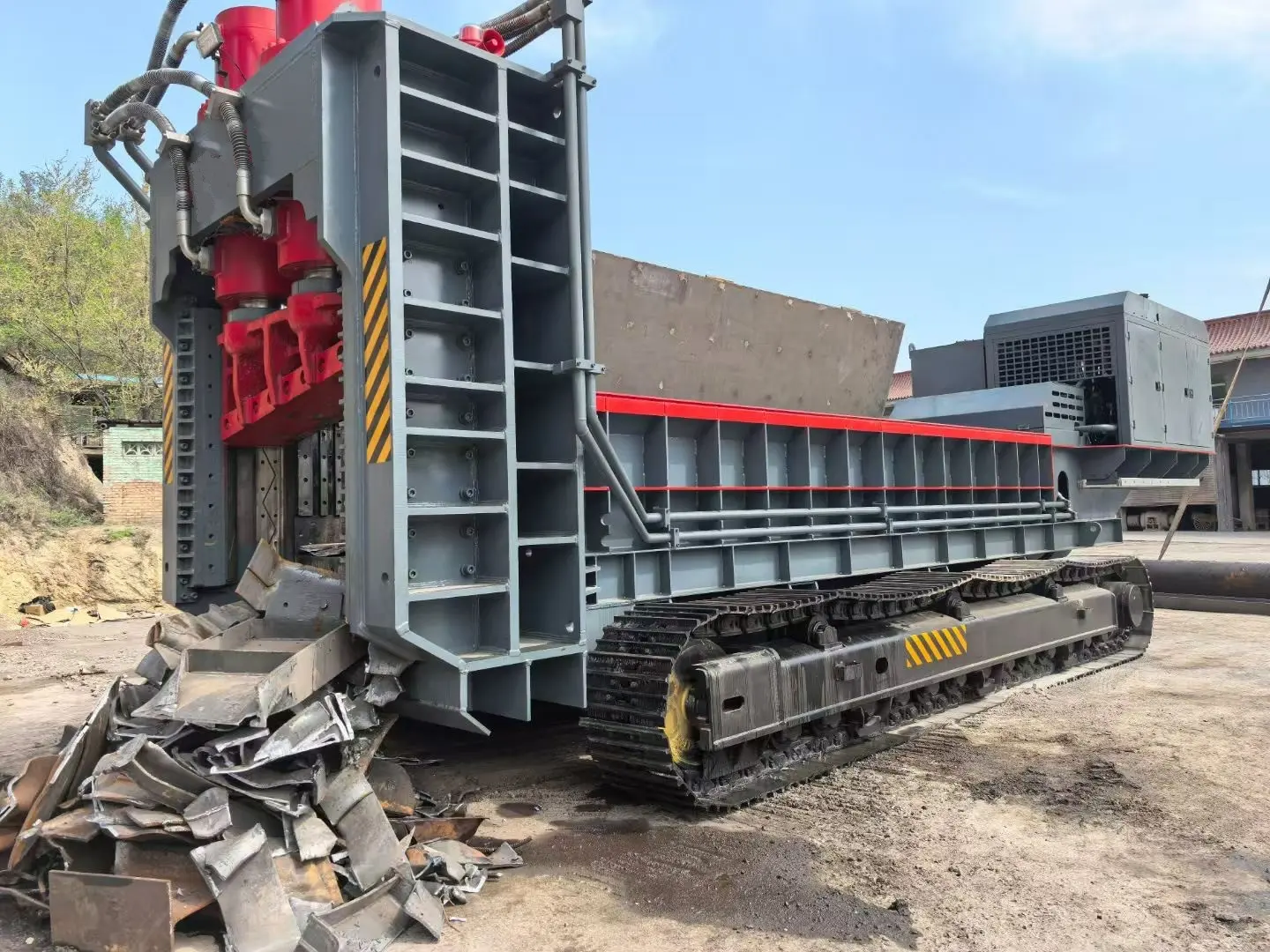
For versatility across different demolition jobs, a multi-quick processor often fits best. The attachment's interchangeable jaws handle numerous materials. The jaw types include crushers, pulverizers, a combination of both, and steel-cutting jaws. Some manufacturers offer additional specialty options, such as jaws for cutting through timber in the forest industry; jaws for cutting steel tanks, pipes and vessels; and highly powerful jaws for heavily reinforced concrete.
While multi-quick processors may cost more than other attachments, approximately 15 to 20 percent more than crushers, for example, they more than make up for that difference in their versatility, achievable through the interchangeable jaw sets.
Powered Up
After determining the best type of attachment for the job, consider the technology powering the tool. Cylinders power demolition attachments, and typically the larger the cylinder, the more powerful the tool. Because of this, contractors seeking more demolition power in the past had to buy or rent a larger excavator to handle the larger attachment. That's no longer the case.
As manufacturers incorporate more technology into attachments, some are achieving as much as 25 percent more power without increasing the cylinder size. To pull this off, manufacturers build additional chambers into the cylinder to allow for as much as 20 percent more surface area. Often, this results in an attachment with the same power as a tool two sizes larger. For example, for a crusher, it means that a section of concrete that may take a competitive attachment five or six “bites” to break through, only takes the tool with the enhanced cylinder technology one or two.
This technology gives contractors access to higher crushing and cutting forces they previously couldn’t have had without the huge expenses of a larger tool, as well as a bigger carrier to operate that tool. Larger carriers also come with higher operating costs. The high power-to-weight ratio — higher on attachments with this technology than any other tool in its size class — also opens the door to more efficient high-reach demolition. This is both because contractors can use smaller carriers and because the attachment's lightweight and superior cylinder technology improve tool performance and fuel efficiency.
Some attachments with innovative cylinder technology reduce carrier fuel consumption by up to 20 percent compared to other models. In some cases, the attachment’s efficient design allows it to function normally when the carrier is set in economy mode, achieving the same performance as competitive attachments on an excavator running at full throttle.
In addition, this advanced cylinder technology allows manufacturers to design high-performing attachments. When combined with double-acting speed valves, the advanced attachment designs not only offer improved power and efficiency but also improved productivity. Together, the enhanced cylinder design and double-acting speed valves deliver faster cycle times — from 3.8 seconds to 5 seconds on bigger tools — and as much as 20 percent more power than conventional cylinders.
If the Tool Fits
Of course, the best attachment in the world still needs a suitable carrier to perform well. Make sure to match the attachment to the carrier size and weight. Heavier attachments, naturally, require larger, heavier carriers, which cost more to operate. Too heavy an attachment can cause excessive wear to the excavator and will affect performance. In addition, tools that are too heavy for a machine are a safety risk for other workers near the carrier, while an attachment that is too small reduces productivity.
Also ensure the carrier has enough hydraulic capacity to feed the attachment. Inadequate flow or hydraulic pressure will slow the tool’s cycle times, reducing productivity. Too little pressure also results in less closing force or torque, depending on the attachment.
Another item to check is the attachment's hydraulic circuit requirements. Is the excavator equipped with enough auxiliary hydraulic circuits for the attachment? For example, rotation shears and multi-quick processors require two double-acting hydraulic circuits, one circuit for opening and closing the jaw and one for 360-degree rotation. Attachments that don't rotate, such as static pulverizers or shears, only require one double-acting circuit.